For as long as humans have seen birds, we have dreamed of flying. But turning those dreams into metal, carbon fiber, and jet fuel takes more than just imagination it takes the precise, disciplined mind of an aeronautical engineer.
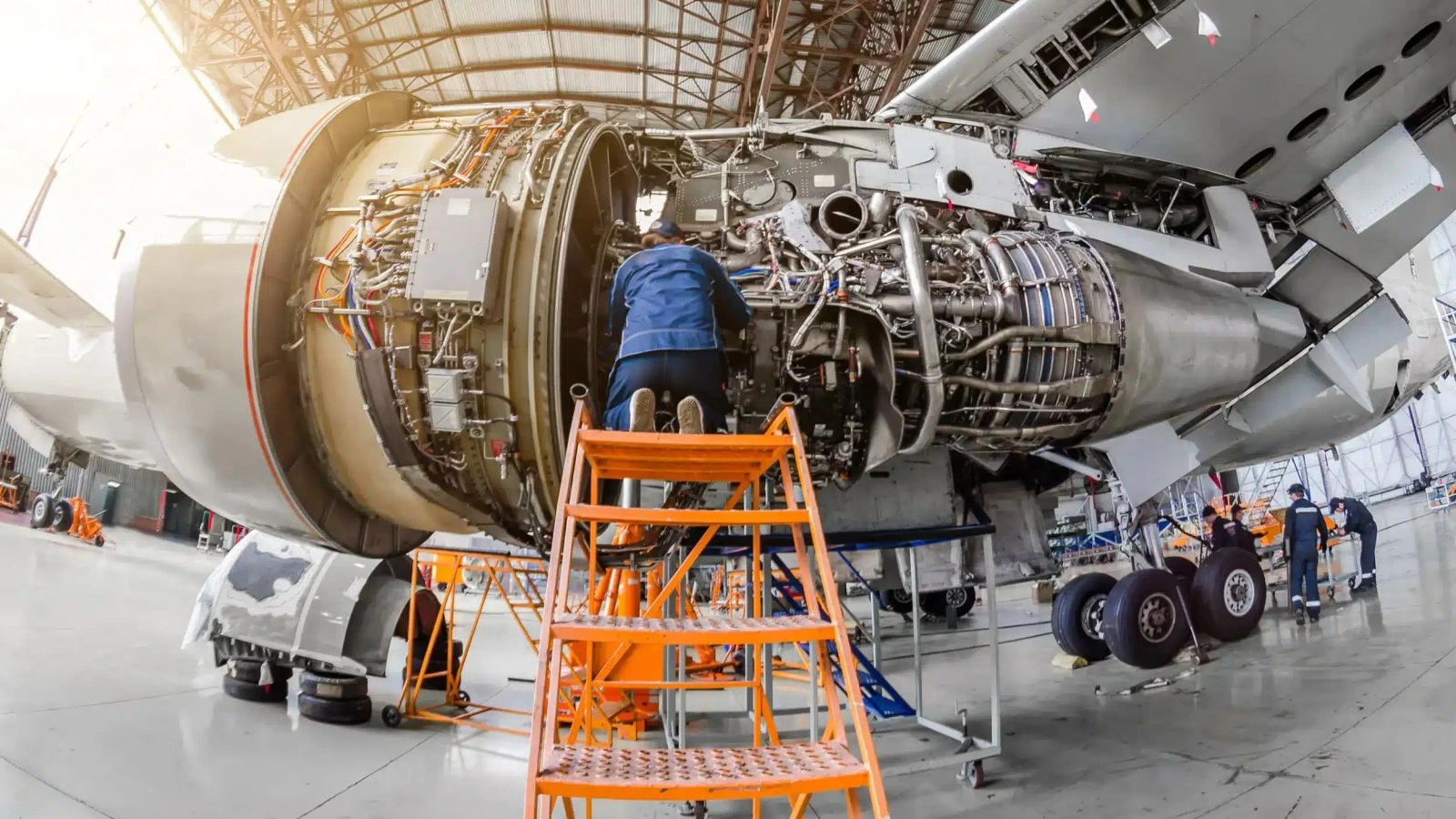
An aeronautical engineer is an architect of the sky. They are professionals responsible for the design, development and maintenance of aircraft that remain in the Earth’s atmosphere. If you’ve ever marveled at the beauty of a Boeing 787 or the agility of a fighter jet, witness the craftsmanship of these brilliant minds.
What Exactly Does an Aeronautical engineer Do?

At its center, the function of an aerospace engineer is to apply the laws of physics and substances technology to create flying machines which are secure, efficient, and progressive. Their paintings isn’t always pretty much making matters fly; it’s approximately making them fly better, faster, and more sustainably.
Furthermore, these engineers should ensure that every layout complies with rigorous global safety requirements. This regularly entails staying updated with the ultra-modern regulatory updates. For example, an engineer ought to be acquainted with each applicable aeronautical information circular (AIC) issued through civil aviation authorities. Just as investors closely monitor Indigo BSE Sensex trends to make informed decisions in the aviation market, engineers rely on these circulars, which provide essential data concerning administrative topics, safety protocols, and adjustments in flight tactics that can directly impact how an aircraft is designed or maintained.
Educational path to become an aeronautical engineer
You cannot become an aeronautical engineer overnight. It is a high-risk profession that requires a solid foundation in mathematics and science.
Higher education
The first step is almost always a bachelor’s degree in aeronautical or aerospace engineering. During these four years, students delve into topics such as thermodynamics, fluid mechanics, propulsion and structural analysis. It is during this time that aspiring engineers learn to calculate lift, drag and thrust, the three pillars of flight.
Specialization and practice
Many students choose to specialize during their later years of study. You can focus on “Avionics” (electronic systems used on aircraft) or “Aerodynamics”. It is important to get an internship while you are at school. Working with companies like Boeing, Airbus or NASA gives a student real-world experience that no classroom can easily replicate.
Essential skills for the modern aerospace engineer
While a degree gets you in the door, specific soft and hard skills will define your success as an aeronautical engineer.
- Design Offices: This is where the conceptualizing happens. Using sophisticated software, engineers create digital twins of aircraft to simulate performance before a single piece of metal is cut.
- Manufacturing Plants: Engineers here oversee the assembly of the aircraft, ensuring that the theoretical design is being executed perfectly on the factory floor.
- Research Facilities: Often funded by governments, these engineers work on the “next big thing,” such as hydrogen-powered engines or supersonic commercial travel.
- Maintenance and Repair Organizations (MROs): Here, the aeronautical engineer ensures that existing fleets remain airworthy and safe for passengers.
Understand Salaries and Benefits for Aeronautical Engineer
One of the main drivers for entering this field besides the passion for flying is the financial reward. Because the job requires high technical competence and considerable responsibility, the compensation is generally very high.
Salaries for aeronautical engineer wage are affected by many factors, including geographic location, years of experience, and specific sector of the industry. Entry-level engineers in the US or Europe can expect a very comfortable starting salary, often significantly higher than the national average for other bachelor’s degree holders.
Difference Between Aeronautical and Aerospace Engineering
An aeronautical engineer focuses specifically on aircraft that operate within the Earth’s atmosphere. This includes commercial aircraft, helicopters, drones and private jets.
An aerospace engineer is a broad term that includes both aeronautical engineering and aerospace engineering (the science of spacecraft that operate outside our atmosphere, such as satellites and Mars rovers). If your passion is strictly for airplanes and the blue sky, you’re looking at the path of an aeronautical engineer. Just as aerospace engineers calculate orbital paths and distances including considerations like the Circumference of earth aeronautical engineers must understand the physics and geometry that govern flight within our atmosphere.
Is a Career as an Aeronautical Engineer Right for You?
Choosing to become an aeronautical engineer is a commitment to lifelong learning. This is a career for people who love to solve puzzles and are not afraid of complex mathematics.
Rewards abound. Aside from a lucrative flight aeronautical engineer wage, there is a unique sense of pride that comes from watching the machine you helped design take off from the runway and disappear into the clouds. You contribute to a global infrastructure that connects families, runs businesses, and explores the unknown an infrastructure that can also be affected by factors like the Donald Trump tariffs impact on global trade, which influenced supply chains, aircraft manufacturing costs, and international aviation markets.
Frequently Asked Questions(FAQ)
1. What does an aeronautical engineer do?
An aeronautical engineer designs, develops and tests airplanes, helicopters, drones and their components. They work to improve the performance, safety, fuel efficiency and aerodynamics of flying machines.
2. How much does NASA pay aeronautical engineers?
Aeronautical or aerospace engineers at NASA in the United States typically earn six-figure salaries, with many ranging from around $100,000-$140,000 per year, depending on experience and role.
3. Is aeronautical engineering a good salary?
Yes, aeronautical engineering pays well, especially with experience and expertise. Entry-level engineers earn competitive salaries.
4. Can I join aeronautical after 12th?
Yes, you may be a part of aeronautical engineering after twelfth by deciding on Physics, Chemistry, and Mathematics (PCM) for your better secondary. Admission typically requires clearing entrance exams like JEE, BITSAT, or country-degree engineering exams.
5. Do I need JEE for aeronautical engineering?
You don’t always need JEE for aeronautical engineering but it is required for admission to top institutes like IITs. Many universities and private colleges also accept state or college-specific entrance exams.

Leave feedback about this